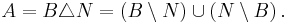Regularity theorem for Lebesgue measure
In mathematics, the regularity theorem for Lebesgue measure is a result in measure theory that states that Lebesgue measure on the real line is a regular measure. Informally speaking, this means that every Lebesgue-measurable subset of the real line is "approximately open" and "approximately closed".
Statement of the theorem
Lebesgue measure on the real line, R, is a regular measure. That is, for all Lebesgue-measurable subsets A of R, and ε > 0, there exist subsets C and U of R such that
- C is closed; and
- U is open; and
- C ⊆ A ⊆ U; and
- the Lebesgue measure of U \ C is strictly less than ε.
Moreover, if A has finite Lebesgue measure, then C can be chosen to be compact (i.e. – by the Heine-Borel theorem – closed and bounded).
Corollary: the structure of Lebesgue measurable sets
If A is a Lebesgue measurable subset of R, then there exists a Borel set B and a null set N such that A is the symmetric difference of B and N: